Based on the characteristics of stability, environmental protection and high temperature resistance, silicone rubber products have become indispensable partners in our life, from kitchen utensils, toys to cars, medical supplies and so on. This article will take you to learn more about silicone rubber.
1. What Is Silicone Rubber?
Silicone rubber is a high-performance synthetic elastomer. It has many desirable properties, making it perfect to use in countless applications. It shows durability, high viscosity, elasticity, and heat resistance, among other impressive feats.
![]()
This durable elastomer has uses in almost every industry and sector. They can be made into different shapes and designs. Because of this adaptability, they’re used in industries like electronics, medical, construction, and many others.
2. What Are The Major Types of Silicone Rubber?
Based on the processing method used on the silicone rubber. The three major types will be HTV, LSR, RTV. Let’s look at each one in detail.
High-Temperature Vulcanized (HTV)
HTV solid silicone rubber contains long-chained polymers with heavy molecular weight. You can have them in an unprocessed form. But, you need to vulcanize them under temperatures used for traditional rubbers.
- Characteristics of HTV
![]() HTV has the best in terms of temperature resistance. It’s the go-to choice when you need to retain the original shape under very high thermal extremes. Due to its high compression set, you can find HTV in many high-performing applications, from aerospace to chemicals.
HTV has the best in terms of temperature resistance. It’s the go-to choice when you need to retain the original shape under very high thermal extremes. Due to its high compression set, you can find HTV in many high-performing applications, from aerospace to chemicals.
This variant also has high chemical resistance. It’s shown to resist many compounds and chemical reagents. HTV’s electrical properties are also favorable. High-temperature dielectric performance beats general rubber by a considerable margin. Plus, it’s also a good insulator.
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR)
LSR has the most miniature polymer molecular chain out of the three major types. It has a low molecular weight, with better flow properties than HTV. You can extrude or inject mold into it using specialized equipment.
- Characteristics of LSR
![]() LSR has a unique chemical property consisting of a chain of molecules called a siloxane bond. This bond type has higher bonding energy compared to its carbon counterpart. This elastomer type also maintains its original physical properties under extreme conditions.
LSR has a unique chemical property consisting of a chain of molecules called a siloxane bond. This bond type has higher bonding energy compared to its carbon counterpart. This elastomer type also maintains its original physical properties under extreme conditions.
Because of its versatility, you can apply it to various industrial uses. You can use it for food-grade to automotive applications. LSR is hypoallergenic and biocompatible, which complies with FDA standards.
Room Temperature Vulcanized (RTV)
RTV is a type of silicone rubber you can cure at room temperature. It can either be one (RTV-1) or a mixture of two (RTV-2) polymers where hardness ranges from soft to medium. It consists of silicone polymers, fillers, and catalysts formed with a Si-O bond.
- Characteristics of RTV
![]() RTVs have excellent release properties compared to traditional rubber mode. It also has high-temperature and chemical resistance, making it ideal for several functions.
RTVs have excellent release properties compared to traditional rubber mode. It also has high-temperature and chemical resistance, making it ideal for several functions.
RTVs are perfect as sealants and encapsulations. It’s also widely used for art-related applications like prototypes and sculptures. And you could also find it in spaces like automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
3. What are the Components of Silicone Rubber?
Silicone rubber is identified as an elastic polymer since it possesses viscoelasticity. It is synthetically made by mixing various materials. The elements silicon, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen make up Silicone itself.
Silica
Silicone rubber’s primary ingredient is silica, a naturally-occurring form of sand. The process of making silicone involves extracting the essential element silicon from silica. It then passes through hydrocarbons and mixes with other chemicals.
Methyl Chloride
![]() After extracting the silicon from the raw silica material, it is mixed with methyl chloride and heated. This action produces methyl chlorosilane, which contains dimethylsiloxane.
After extracting the silicon from the raw silica material, it is mixed with methyl chloride and heated. This action produces methyl chlorosilane, which contains dimethylsiloxane.
Poly-dimethylsiloxane
![]() Poly-dimethylsiloxane is the most predominant silicone chemical compound. It defines silicone’s central characteristics and contains the siloxane bond.
Poly-dimethylsiloxane is the most predominant silicone chemical compound. It defines silicone’s central characteristics and contains the siloxane bond.
The Siloxane “Backbone”
![]() The siloxane bonds (–Si–O–Si–) form the silicone backbone. It is highly flexible and stable even in extreme temperatures. Its binding energy comes at 433 kJ/mol, which tops carbon bonds only at 355 kJ/mol. This composition allows silicone rubber to have heat resistance and chemical stability properties.
The siloxane bonds (–Si–O–Si–) form the silicone backbone. It is highly flexible and stable even in extreme temperatures. Its binding energy comes at 433 kJ/mol, which tops carbon bonds only at 355 kJ/mol. This composition allows silicone rubber to have heat resistance and chemical stability properties.
4. How is Silicone Rubber Made?
Silicone rubber is produced through a series of steps. Industrial silicone manufacturers are the ones that make them in bulk. These manufacturers follow a series of steps using specialized equipment.
Step 1. The first step in silicone rubber production is the isolation of silicon from silica. Manufacturers do this by heating massive volumes of quartz sand at 1800 °C.
The resulting material is pure silicon isolated from the quartz sand. The pure silicon is then cooled and grounded into fine particles.
Step 2. The isolated silicon powder combines with methyl chloride and is heated once more. The heat will set off a reaction between these components, forming methyl chlorosilane. This compound contains dimethyldichlorosilane, the primary building block of silicone.
Step 3. Turning dimethyldichlorosilane into silicone requires distillation. This process separates several components of methyl chlorosilane from one another. Each chlorosilane compound has varying boiling points. So, the mixture heats under a sequence of specific temperatures.
Step 4. After distillation, manufacturers add water to the dimethyldichlorosilane. This action breaks it down into hydrochloric acid and disilanol. The two then condense into poly-dimethylsiloxane.
Step 5. Poly-dimethylsiloxane contains the siloxane “backbone” of silicone. From this compound, you can polymerize silicone based on the properties you need. Polymerization involves different methods depending on the desired product.
5. How is Silicone Rubber Cured?
Silicone rubber is perfect for making molds because of its toughness and flexibility. These silicone molds need curing at certain temperatures to become solid and stable. Curing speed varies depending on the product’s thickness. There are two types of silicone rubber curing: tin and platinum.
Tin (Condensation) Curing
![]() This method uses tin salts as a catalyst. Tin salts don’t respond too much to heat. It uses air moisture to transform mold from liquid to solid. This method produces excellent silicone properties and is less prone to inhibition.
This method uses tin salts as a catalyst. Tin salts don’t respond too much to heat. It uses air moisture to transform mold from liquid to solid. This method produces excellent silicone properties and is less prone to inhibition.
Using a tin catalyst will cure silicone at lower temperatures. But, it may produce higher shrinkage compared to a platinum catalyst. Silicone cured in this method also doesn’t comply with FDA for food or skin applications.
Platinum (Addition) Curing
![]() This curing method uses a platinum catalyst under a high temperature to turn liquid silicone into solid. Increasing the temperature during platinum curing can speed up the process. Every 10 degrees above 70° C reduces curing speed by half.
This curing method uses a platinum catalyst under a high temperature to turn liquid silicone into solid. Increasing the temperature during platinum curing can speed up the process. Every 10 degrees above 70° C reduces curing speed by half.
Platinum cured silicone lasts long. And many are FDA-approved for food and skin use. It also produces tough finishes that are super heat resistant. A downside is that it’s more prone to inhibition. It also requires a very complex mixing process.
6. What are the Typical Properties of Silicone Gel?
Heat and Cold Resistance
Silicone rubbers can take a lot of punishment from extreme temperatures. And without losing their original physical properties. You can use it at 150 °C for a long while, only experiencing slight alterations. It can even withstand 200 °C for thousands of hours. You can’t say the same for other organic rubbers.
- The same goes for cold temperatures. Silicone rubbers won’t reach embrittlements above -70 °C.
- Compare that to your typical organic rubber with embrittlement points ranging from -30 to -20 °C.
Weatherability
Ozone causes rapid deterioration on most organic rubbers. This is not the case for silicone rubber. In fact, ozone has almost zero effects on silicone. It can also easily withstand other weather elements like rain, wind, and UV rays.
Moisture and Steam Resistance
Silicone rubber has a 1% water absorption. You can submerge it in water for long periods and maintain its original properties. It’s also resistant to steam under normal pressure. But, as steam pressure increases, the more it will react. Deterioration begins upon reaching high steam pressures at 150 °Celcius. But you can bypass this weakness by making changes in the silicone rubber formula. You can also couple it with the right curing agent that’s water and steam-resistant.
Resistance to Oils, Solvents, & Other Chemicals
Silicone products have exceptional chemical resistance. It can withstand interaction with oil at temperatures above 100 °Celcius. Solvents and other chemicals also have little effect on silicone rubbers.
Polar organic compounds or dilute acids/bases may cause swelling, but only at up to 15% of volume. Unlike ordinary rubber, silicone won’t dissolve. And it will return to its original state if you remove it from the solvent.
Electrical Insulation
This synthetic elastomer is an ideal insulating material. Its insulation resistance comes in at 1TΩm – 100TΩm. You can expect it to remain stable over a wide range of temperatures, regardless of the frequency spectrum. Because of this impressive feat, it saw extensive use in many electrical applications.
Thermal Conductivity
Silicone rubber has a much higher thermal conductivity than organic rubber. This makes them ideal for use in heat removal products (think thermal sheets). Some products even use filler that further improves thermal conductivity.
Flame Retardance
You can incorporate flame retardancy into rubbers to make them more combustion-resistant. Silicone rubbers tend to resist fire. But, once ignited, it will continue to burn. You can generate fire-resistant properties by adding flame retardant to the product.
If you manage to ignite one, it won’t emit harmful black smoke like those from organic polymers. Some products have even received a UL94 V-O certification. This stamp signifies that these rubbers can withstand specific flame exposures without burning.
Electrical Conductivity
Your standard silicone rubber can insulate electricity and heat. But, there are conductive variants available. Conductive silicone rubbers also have the properties of typical variants. The key difference is that they have materials like carbon, which adds conductivity.
Compression Set
Compression set is a material’s ability to return to initial thickness after compressive stress at specific temperatures. A valuable quality of silicone rubber is its consistent compression set. This characteristic remains true over an extensive temperature range (-60 °C to 250 °C).
Silicone rubbers can maintain a compression set not seen in ordinary organic rubber. You can also make products with low compression sets if needed. Manufacturers do this via post-curing and choosing suitable curing agents.
Tear Strength and Tensile Strength
The tear strength of silicone rubber is somewhere around 9.8 kN/m. But it’s possible to manufacture rubbers with tear strengths of up to 49 kN/m. You modify the polymer and select the proper fillers and crosslinkers.
High-tear strength rubbers are ideal for high-tension applications. These rubbers see extensive use in the automotive and medical industries.
Flex Fatigue Resistance
Silicone rubbers can resist a wide service temperature range. But, their flex fatigue resistance is no different from organic rubbers. Flex fatigue resistance is the ability of rubber to withstand bending and flexing.
Still, there are some manufacturers out there who’ve ameliorated this limitation. More and more products are now becoming flex fatigued resistant. Even as high as ten times the usual resistance rate.
Gas Permeability
Silicone rubber is one of the most permeable synthetic polymers. Many applications, especially those in extreme environments, require permeability. Permeability makes silicone products excellent barriers against various types of gasses. These rubbers also possess selectivity, making them beneficial for multiple uses.
Transparency and Coloring Properties
Silicone comes in varying pigmentations, but you can produce it as clear and transparent. Silica is a mineral from which silicone derives. This mineral is the reason silicone can maintain its transparency. You can use transparent silicone as a cover to enhance cosmetic appeal. It’s commonly applied as overlays and equipment covers.
Radiation Resistance
Some formulations, like Methylphenyl silicone rubber, can resist radiation. This quality makes these elastomers excellent components for cables and connectors in nuclear plants. On the other hand, general silicone doesn’t possess radiation resistance, much like organic rubber.
Vibration Absorption
There are silicone rubber variants that come with vibration absorption characteristics. These products can absorb vibration at an extensive temperature range (-50°C to 100 °C). You can use these products as ideal vibration insulators.
Releasability and Non-Corrosivity
Polymers are typically non-corrosive. Silicone rubbers, in particular, are chemically inert. This means that these materials are stable and non-reactive under certain conditions. Many industries use certain types of silicone because of their non-corrosive properties.
Physiologically Inert
Unlike other organic rubbers, silicone has minimal effects when placed in contact with biological tissue. It’s physiologically inert and suitable for medical uses and baby products. Silicone is also comfortable to the touch, which suits it for eyewear products and leisure apparel.
7. What Are The Essential Applications of Silicone Rubber?
As you already know, silicone has many beneficial properties. These attributes make silicone highly suitable for many functions. It’s also widely considered safe for food and medical applications. Here are some of the most common applications of silicone rubber:
Consumer Electronics
![]() Silicone has countless uses in the field of electronics. For example, electronic gadgets use it to seal their inner circuits, acting as protection against wear and tear. It’s also a conventional insulator for many products. Many electronic devices use these rubbers as insulating tapes, coatings, and lubricants. You can find them in ECUs, LED devices, PCB assemblies, and many more.
Silicone has countless uses in the field of electronics. For example, electronic gadgets use it to seal their inner circuits, acting as protection against wear and tear. It’s also a conventional insulator for many products. Many electronic devices use these rubbers as insulating tapes, coatings, and lubricants. You can find them in ECUs, LED devices, PCB assemblies, and many more.
Office Automation Equipment
![]() Office automation devices like printers and copiers rely on rollers to carry out their functions. Silicone rubber can improve the efficiency of these rollers. Remember, these elastomers have a good compression set and can also have thermal and electric conductivity. These attributes make them ideal as rollers that improve equipment efficiency.
Office automation devices like printers and copiers rely on rollers to carry out their functions. Silicone rubber can improve the efficiency of these rollers. Remember, these elastomers have a good compression set and can also have thermal and electric conductivity. These attributes make them ideal as rollers that improve equipment efficiency.
Automobiles
![]() Silicone delivers the durability and strength needed by many automotive applications. It’s no wonder the automotive industry has extensive use for silicone materials. Many functions produce heat, making these products suitable for heat-resistant parts and accessories. You can find them in seals, gaskets, o-rings, and engine mounts.
Silicone delivers the durability and strength needed by many automotive applications. It’s no wonder the automotive industry has extensive use for silicone materials. Many functions produce heat, making these products suitable for heat-resistant parts and accessories. You can find them in seals, gaskets, o-rings, and engine mounts.
Electrical Wirings
![]() Silicone has many properties that make it suitable for electrical wirings. It has heat and cold resistance, excellent insulating characteristics, and chemical stability. These properties allow silicone wires to have a long service life in high-voltage applications.
Silicone has many properties that make it suitable for electrical wirings. It has heat and cold resistance, excellent insulating characteristics, and chemical stability. These properties allow silicone wires to have a long service life in high-voltage applications.
Machinery
![]() From factory and medical equipment to machines that we use day-to-day, you can bet silicone is an integral component. For many applications, silicone acts as a sealing and insulating agent. Silicone is an essential element of many commercial manufacturing machines. You can find them in all types of equipment, whether manually operated or automatic.
From factory and medical equipment to machines that we use day-to-day, you can bet silicone is an integral component. For many applications, silicone acts as a sealing and insulating agent. Silicone is an essential element of many commercial manufacturing machines. You can find them in all types of equipment, whether manually operated or automatic.
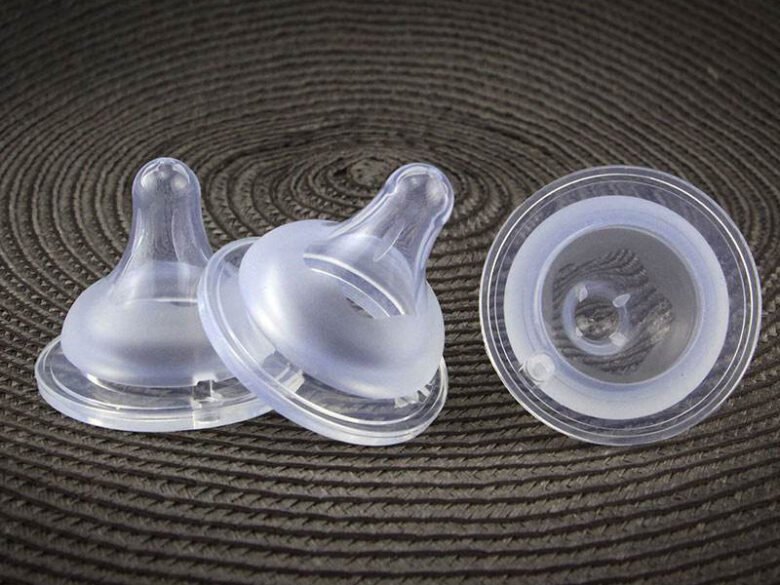
Food Applications
![]() Silicone is widely considered safe for food applications. Ever noticed silicone in all types of food packaging and cookware? You can even make baby bottle nipples out of silicone. Food processing equipment makes use of these polymers all the time. You’ll see them as tubes, seals, gaskets, and sheets for food manufacturing equipment.
Silicone is widely considered safe for food applications. Ever noticed silicone in all types of food packaging and cookware? You can even make baby bottle nipples out of silicone. Food processing equipment makes use of these polymers all the time. You’ll see them as tubes, seals, gaskets, and sheets for food manufacturing equipment.
8. What's the Difference Between Rubber and Silicone Rubber?
Both rubber and silicone are elastomers, but they differ in atomic structure. The main difference between the two is their constructive “backbone.”
![]()
Rubber has carbon bonds, while silicone has oxygen and silicon serving as bonds. That’s from a scientific point of view.
From a performance point of view, silicone trumps rubber in almost every way. As mentioned above, silicone is far superior when it comes to:
- Extreme temperature resistance
- Durability
- Weather-ability
- Chemical stability
- Flame retardancy
- Electrical insulation
- And many more
9. What's the Difference Between Plastic and Silicone Rubber?
Plastic and silicone have always been used as an alternative over the other. You can shape both of these materials into any form. Yes, plastics are inexpensive and long-lasting. And you can also say it has pretty similar characteristics to silicone. But silicone outperforms plastic in many critical functions. Think of silicone as an upgrade to plastic in terms of performance.
One notable advantage of silicone over plastic is its non-toxicity. We’re all aware of the adverse environmental effects of plastics. Silicone is no doubt a more eco-friendly alternative. It doesn’t degrade into smaller pieces and doesn’t release harmful toxins when burned.
10. Is Silicone Rubber in High Demand?
![]() Because of its multi-industry benefits, silicone demand only grows each year. According to Globe Newswire, the global LSR market size may reach over USD 4.0 Billion by 2028. And that’s just liquid silicone rubber alone.
Because of its multi-industry benefits, silicone demand only grows each year. According to Globe Newswire, the global LSR market size may reach over USD 4.0 Billion by 2028. And that’s just liquid silicone rubber alone.
Silicone rubber has been increasing demand in many major sectors, particularly healthcare. It’s pretty clear given its superiority to both organic rubber and plastic. Silicone rubber is more durable with better resistance to chemicals and extreme temperatures. These characteristics drive demand for silicone-based materials.
Many companies are also fine-tuning and growing their research and development. These initiatives aim to push for product innovation and expects to drive demand for silicone products.
11. Who Are the Largest Manufacturers of Silicone Rubber?
Demand presents many revenue opportunities for silicone rubber manufacturers. And according to research, the industry expects to grow within the next few years. Here are the largest silicone rubber manufacturers competing in the global market.
The Dow Chemical Company
The Dow company is a leading manufacturer of silicone-based products for various applications. It provides solutions to the textile, automotive, healthcare, and electronics industries. Dow’s innovative products come under the names Silastic, XIAMETER, and SYLGARD. Apart from silicone, it offers other chemical and agricultural solutions.
Wacker Chemie
Wacker is another leading brand in the global silicone market. It produces an array of silicone-based products for several industries. Its lineup includes silicone rubbers, fluids, resins, and other hybrid silicone materials. Wacker also provides other specialty chemicals and elastomers for industrial and personal use.
Shin-Etsu Chemical
Shin-Etsu is a notable developer of silicones used for diverse purposes. This manufacturing giant focuses on several industries, from automotive to paper. It’s also a chief global producer of semiconductor silicon wafers, PVCs, and adhesives. Commercial applications include electronic devices, cosmetic ingredients, and environmentally-friendly alternatives to familiar products.
The Elkem Group
Elkem is a company that develops and manufactures silicones and other polymer solutions. It’s been catering to multiple industry needs since 1904. And it already boasts 26 manufacturing sites. It serves various industries, including aerospace, cosmetics, paper, and textiles.
12. Why Choose GX Silicone?
The answer is simple. GX Silicone maintains laser focus on providing top-quality silicone-based silicone rubber materials. We’ve only been around since 2007. But we’ve already grown into a firm with a track record of unsurpassed product quality. We offer silicone products for diverse markets, including:
- Electronics
- Medical
- Mechanical engineering
- Food-grade
- Automotive
- And many more
Unlike many competitors, our sole focus is on silicone-based compounds. We believe that focusing solely on this polymer segment lets us develop products that stand out in a big way. With an extreme dedication to research and development, expect us to provide the best the current market offers.
Want to learn more about how we help? Contact GX Silicon today!